Hyperbolic geometry in simple words
In The Elements, Euclid builds up his geometry on the following axioms:
- «A straight line segment can be drawn joining any two points.»
- «Any straight line segment can be extended indefinitely in a straight line.»
- «Given any straight line segment, a circle can be drawn having the segment as radius and one endpoint as center.»
- «All right angles are congruent.»
- «In a plane, given a line and a point not on it, at most one line parallel to the given line can be drawn through the point.»
Hyperbolic geometry arose in the 19th century, when mathematicians started to question the fifth axiom.
The problem of the parallel postulate
In the ancient Greece, Euclid’s axioms and the geometry that they imply, appeared so much in harmony with the reality that they were accepted as universal truths. From this conviction resulted twenty-three centuries of monopoly for Euclidean geometry.
However, during this period several mathematicians believed that the fifth axiom, also called the parallel postulate, was a theorem. In other word, they were trying to prove the parallel postulate using the first four axioms. On the other hand, if the converse would have been true i.e if it would have been a true axiom. Then, the door would have been open to non-Euclidean geometry based on different axioms.
As a consequence, the parallel postulate was a concern for thinkers away from mathematics. For centuries, philosophers and theologians had build systems up on Greek mathematics and logic. To open the door to new geometries would have shake the basis of these systems.
In the years 1830’s, Bolay and Lobachevsky independently gave a proof of the fact that the fifth axiom is indeed an axiom. To do so they built a non-Euclidean geometry i.e a geometry in which the axiom of parallel is not satisfied. This geometry had been called later on hyperbolic geometry.
In fact, Riemann works showed that hyperbolic geometry is only one geometry among an infinite set of non-Euclidean geometries. However, it took a long while to the entire academic community to recognize these new geometries. With the mathematical work of Poincaré, hyperbolic geometry gained a good reputation and has been the source of many progress in mathematics and physics during the 20th century.
The Poincaré model of hyperbolic geometry
Hyperbolic geometry sits inside a disk of Euclidean radius 1. However, one must forget that the disk is Euclidean and consider it only by itself. As suggested by the custom, we designate by \(\textbf{H}\) the disk equipped with the hyperbolic structure and by \(\partial \textbf{H}\) the boundary of the disk which is a circle of Euclidean radius 1. The Poincaré model of hyperbolic geometry relies on the following principle:
- «In \(\textbf{H}\), the shortest path between two points is the circle orthogonal to \(\partial \textbf{H}\) and passing through these two points.»
In the preceding statement, a diameter of the disk is considered as a circle of infinite radius orthogonal to \(\partial \textbf{H}\). Thus, in \(H\) the straight line is not the shortest path between two points. Except if the two points lie on a diameter.
From now on, the shortest paths between two points in \(H\) play the role of the line segments in the Euclidean plane. We call these curves the \(geodesics\) of H. With the preceding principle, we can observe that in \(H\) the axiom of parallel is not satisfied. Namely:
- «given a geodesic and a point not on it, there exists infinitely many geodesics parallel to the given geodesic.»

- All the green geodesics are parallel to \(\Delta\) and pass through \(P\).
A surprising feature of the geometry in \(H\), is that if you move an object from the center of the \(H\) in direction of \(\partial \textbf{H}\) the object appears to be smaller and smaller. This impression comes from a Euclidean interpretation of hyperbolic geometry. From a Euclidean point of view the object get smaller but, from a hyperbolic point of view, the size of the object is constant.

- All these pentagons have same hyperbolic area and lie at an infinite hyperbolic distance of \(\partial \textbf{H}\).
To understand that, imagine you are this object and as you get closer to \(\partial \textbf{H}\), the space around you is contracted. Indeed for someone looking at you from above you look smaller. But inside the hyperbolic world, the measuring tape you us also gets smaller and you cannot realize that you are shrinking.
Likewise, every step you make in direction of \(\partial \textbf{H}\) is smaller than the previous one. This decrease is even exponential and after 10,000 steps in direction of \(\partial \textbf{H}\), the circle will appear to you as far as before. Even if \(\textbf{H}\) sits in a Euclidean disk of finite area, its infinite from the intrinsic hyperbolic point of view.
Hyperbolic triangles
The shape of the triangles is another remarkable feature of \(\textbf{H}\). In particular, if $=\(T\) is a hyperbolic triangle of angles \(\alpha\), \(\beta\) and \(\gamma\) then
- \(\alpha +\beta + \gamma< \pi\).
The hyperbolic disk even contains ideal triangles that are obtained as limits of increasing sequences of triangles. All these ideal triangles are isometric and of finite hyperbolic area. In other word, in the hyperbolic disk, we cannot build triangles of arbitrary large area.
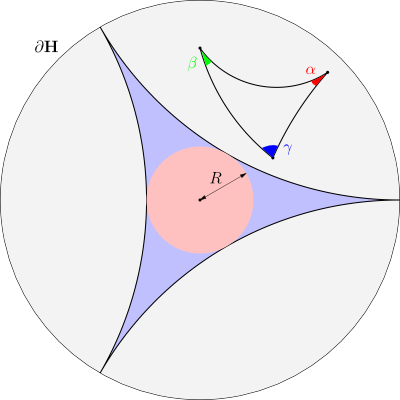
- In \(H\) any triangle is smaller than an ideal triangle (in blue on the picture).
In addition, triangles are thin in \(\textbf{H}\). This means that there exists a universal constant \(R\) such that for any triangle \(T\) in \(\textbf{H}\) there exists a center \(c_t\) such that the hyperbolic circle \(\mathcal{C}_T\) meets the tree sides of \(T\). This last feature is important because it is used by Gromov to generalize the notion of hyperbolic spaces.
As we saw, hyperbolic geometry is very different from Euclidean one. However, it is important to note that these differences only appear at large scale. Indeed, when you restrain yourself to a very small part of \(\textbf{H}\), the geodesics look like straight lines, the sum of the angles of a triangle is so close to be \(\pi\) and the postulate of parallel seems valid.

- Small hyperbolic triangles look like Euclidean ones.
As a consequence, if you want to know if you live in a Euclidean or a hyperbolic universe, you cannot only draw triangles and parallel lines around you. As the hyperbolic properties appear only at large scale, you may need to draw shortest paths between galaxies. Which will probably make you give up on this project.
After the article «Hyperbolic groups» of M. Gromov, a hyperbolic space is a metric space in which triangles are thin. A group is hyperbolic if it is a certain type of group of symmetries of a hyperbolic space. This article has been very influential in geometric group theory. Indeed, under the hyperbolicity assumption, the geometric properties of the space are closely related to the algebraic properties of the group. See for instance here.
Moreover, given a hyperbolic space \(X\) and following M. Gromov’s approach, it is usually possible to extend and adapt tools and methods of \(\textbf{H}\) to the study of \(X\). This is a very powerful method because the geometry of \(\textbf{H}\) is well known and because the class of hyperbolic spaces is enormous.